Angioplasty Cost in South Korea from top hospitals starts from KRW 24839765 (USD 18500)approx
.Angioplasty is a minimally invasive procedure used to correct the blood flow through the artery, The blood flow may be restricted due to an obstruction or most commonly because of arterial atherosclerosis, that is, the thickening of the arterial wall because of deposits.
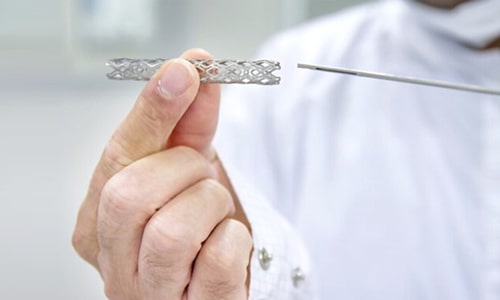
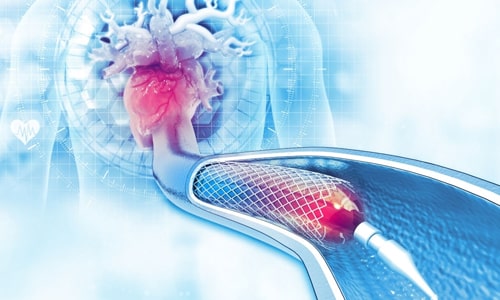
Angioplasty is sometimes also known as percutaneous transluminal angioplasty or balloon angioplasty. During the procedure, a thin tube or catheter is passed through the blood vessel in the groin or arm area to reach the site of narrowing or blockage. A stent or a balloon is attached to the tip of the catheter. After placing the stent or inflating the balloon, the interventional cardiologist withdraws the catheter.
There are different types of angioplasty procedures and each type has a clear indication on when it should be performed. Angioplasty cost also varies as per the type of procedure performed.
The common types of angioplasty and their indications are as follows:
Coronary Angioplasty: It is used in the case of stenosis of narrowing of the coronary artery in the heart due to plaque build-up, leading to unstable angina causing symptoms such as chest pain and functional limitations.
Peripheral Angioplasty: It is used to open the narrowing of other arteries other than the coronary arteries. Examples may include arteries in the abdomen, leg, and kidney.
Carotid Angioplasty: It is used to treat carotid artery stenosis, the main artery in the neck that supplies blood to the brain and face.
The following factors affect angioplasty cost:
| Country | Cost | Local_currency |
|---|---|---|
| Czechia | USD 8000 | Czechia 181520 |
| Greece | USD 17500 | Greece 16100 |
| India | USD 3600 | India 299340 |
| Israel | USD 18000 | Israel 68400 |
| Malaysia | USD 9500 | Malaysia 44745 |
| Poland | USD 6000 | Poland 24240 |
| South Korea | USD 18500 | South Korea 24839765 |
| Spain | USD 19500 | Spain 17940 |
| Switzerland | USD 12500 | Switzerland 10750 |
| Thailand | USD 10600 | Thailand 377890 |
| Tunisia | USD 8000 | Tunisia 24880 |
| Turkey | USD 4500 | Turkey 135630 |
| United Arab Emirates | USD 8580 | United Arab Emirates 31489 |
Treatment cost
We provide numerous services for your medical journey, including:
We offer packages at reasonable pricing that include a variety of additional advantages, making it a better deal than paying for individual perks at the hospital. Angioplasty Surgery is required when a person has been diagnosed with blocked or narrowed coronary arteries. It is needed to clear the blockages and ensure restoration of normal blood flow through the vessels and arteries to the heart muscles. The procedure follows an insertion of a thin tube (a catheter) via incision in the leg or arm and guiding it to the heart. Two types of Angioplasties are there- Coronary and Balloon angioplasty. Therefore, the procedure is quite helpful to remove the obstruction or clotting., Consider this comprehensive & discounted package for Angioplasty surgery at Sharda Hospital, India.
MediGence is offering immense facilities for your medical journey such as:
We offer packages at reasonable pricing that include a variety of additional advantages, making it a better deal than paying for individual perks at the hospital. Angioplasty Surgery is required when a person has been diagnosed with blocked or narrowed coronary arteries. It is needed to clear the blockages and ensure restoration of normal blood flow through the vessels and arteries to the heart muscles. The procedure follows an insertion of a thin tube (a catheter) via incision in the leg or arm and guiding it to the heart. Two types of Angioplasties are there- Coronary and Balloon angioplasty. Therefore, the procedure is quite helpful to remove the obstruction or clotting., Consider this comprehensive & discounted package for Angioplasty surgery at Pushpawati Singhania Research Institute, India.

Asan Medical Centre located in Seoul, South Korea is accredited by ISO. Also listed below are some of the most prominent infrastructural details:


Parkway East Hospital located in Joo Chiat Pl, Singapore is accredited by JCI. Also listed below are some of the most prominent infrastructural details:

Types of Angioplasty in Medanta - The Medicity and its associated cost
| Treatment Option | Approximate Cost Range (USD) | Approximate Cost Range (INR) |
|---|---|---|
| Angioplasty (Overall) | 2846 - 6825 | 227416 - 551175 |
| Coronary Angioplasty (PCI) | 4093 - 6861 | 336465 - 560520 |
| Peripheral Angioplasty | 3344 - 5542 | 280602 - 465751 |
| Balloon Angioplasty | 2817 - 4481 | 231626 - 365514 |
DOCTORS IN 14 SPECIALITIES
FACILITIES & AMENITIES

Mount Elizabeth Hospital located in Singapore, Singapore is accredited by JCI. Also listed below are some of the most prominent infrastructural details:

Types of Angioplasty in Apollo Hospitals and its associated cost
| Treatment Option | Approximate Cost Range (USD) | Approximate Cost Range (INR) |
|---|---|---|
| Angioplasty (Overall) | 2809 - 6707 | 234977 - 556673 |
| Coronary Angioplasty (PCI) | 4038 - 6862 | 325439 - 561515 |
| Peripheral Angioplasty | 3394 - 5707 | 275628 - 458912 |
| Balloon Angioplasty | 2785 - 4445 | 232806 - 364115 |
DOCTORS IN 14 SPECIALITIES
FACILITIES & AMENITIES

Types of Angioplasty in Venkateshwar Hospital and its associated cost
| Treatment Option | Approximate Cost Range (USD) | Approximate Cost Range (INR) |
|---|---|---|
| Angioplasty (Overall) | 2550 - 6113 | 208614 - 497880 |
| Coronary Angioplasty (PCI) | 3641 - 6077 | 300040 - 500366 |
| Peripheral Angioplasty | 3047 - 5057 | 250332 - 417474 |
| Balloon Angioplasty | 2534 - 4055 | 207905 - 332715 |
DOCTORS IN 13 SPECIALITIES
FACILITIES & AMENITIES

Gleneagles Hospital located in Napier Road, Singapore is accredited by JCI. Also listed below are some of the most prominent infrastructural details:

Types of Angioplasty in Star Hospitals and its associated cost
| Treatment Option | Approximate Cost Range (USD) | Approximate Cost Range (INR) |
|---|---|---|
| Angioplasty (Overall) | 2318 - 5659 | 193198 - 456893 |
| Coronary Angioplasty (PCI) | 3398 - 5611 | 275956 - 462126 |
| Peripheral Angioplasty | 2820 - 4674 | 229343 - 380978 |
| Balloon Angioplasty | 2320 - 3790 | 190288 - 305544 |
DOCTORS IN 12 SPECIALITIES
FACILITIES & AMENITIES

Types of Angioplasty in Global Health City and its associated cost
| Treatment Option | Approximate Cost Range (USD) | Approximate Cost Range (INR) |
|---|---|---|
| Angioplasty (Overall) | 2753 - 6745 | 232671 - 544516 |
| Coronary Angioplasty (PCI) | 4044 - 6642 | 336523 - 560469 |
| Peripheral Angioplasty | 3315 - 5635 | 275082 - 471475 |
| Balloon Angioplasty | 2823 - 4440 | 231582 - 362692 |
DOCTORS IN 14 SPECIALITIES
FACILITIES & AMENITIES

Types of Angioplasty in Primus Super Speciality Hospital and its associated cost
| Treatment Option | Approximate Cost Range (USD) | Approximate Cost Range (INR) |
|---|---|---|
| Angioplasty (Overall) | 2549 - 6100 | 208919 - 499214 |
| Coronary Angioplasty (PCI) | 3647 - 6063 | 298940 - 497303 |
| Peripheral Angioplasty | 3031 - 5089 | 248519 - 414829 |
| Balloon Angioplasty | 2528 - 4066 | 208720 - 333622 |
DOCTORS IN 13 SPECIALITIES
FACILITIES & AMENITIES

Types of Angioplasty in Fortis Malar Hospital and its associated cost
| Treatment Option | Approximate Cost Range (USD) | Approximate Cost Range (INR) |
|---|---|---|
| Angioplasty (Overall) | 2532 - 6100 | 207990 - 498041 |
| Coronary Angioplasty (PCI) | 3660 - 6102 | 300823 - 501333 |
| Peripheral Angioplasty | 3045 - 5077 | 249831 - 414997 |
| Balloon Angioplasty | 2528 - 4054 | 208954 - 332409 |
DOCTORS IN 9 SPECIALITIES
FACILITIES & AMENITIES

Types of Angioplasty in Artemis Health Institute and its associated cost
| Treatment Option | Approximate Cost Range (USD) | Approximate Cost Range (INR) |
|---|---|---|
| Angioplasty (Overall) | 2823 - 6697 | 233538 - 555972 |
| Coronary Angioplasty (PCI) | 3961 - 6739 | 328117 - 551406 |
| Peripheral Angioplasty | 3349 - 5684 | 271091 - 462483 |
| Balloon Angioplasty | 2843 - 4510 | 232968 - 365746 |
DOCTORS IN 15 SPECIALITIES
FACILITIES & AMENITIES

Types of Angioplasty in Sterling Wockhardt Hospital and its associated cost
| Treatment Option | Approximate Cost Range (USD) | Approximate Cost Range (INR) |
|---|---|---|
| Angioplasty (Overall) | 2536 - 6109 | 207110 - 500284 |
| Coronary Angioplasty (PCI) | 3657 - 6101 | 298385 - 501192 |
| Peripheral Angioplasty | 3047 - 5092 | 249304 - 414437 |
| Balloon Angioplasty | 2534 - 4052 | 208485 - 333425 |
DOCTORS IN 14 SPECIALITIES
FACILITIES & AMENITIES

Types of Angioplasty in Medicana International Istanbul and its associated cost
| Treatment Option | Approximate Cost Range (USD) | Approximate Cost Range (TRY) |
|---|---|---|
| Angioplasty (Overall) | 3950 - 7209 | 116820 - 215761 |
| Coronary Angioplasty (PCI) | 5124 - 7249 | 155899 - 219920 |
| Peripheral Angioplasty | 4466 - 6879 | 134449 - 199848 |
| Balloon Angioplasty | 3999 - 6163 | 119944 - 189655 |

Types of Angioplasty in Memorial Antalya Hospital and its associated cost
| Treatment Option | Approximate Cost Range (USD) | Approximate Cost Range (TRY) |
|---|---|---|
| Angioplasty (Overall) | 4008 - 7312 | 117009 - 218899 |
| Coronary Angioplasty (PCI) | 5123 - 7161 | 155094 - 221165 |
| Peripheral Angioplasty | 4547 - 6774 | 134980 - 202910 |
| Balloon Angioplasty | 3996 - 6252 | 118394 - 184766 |
Coronary artery disease (CAD) is one of the most common heart diseases reported across the world. It results due to blood clot formation and plaque accumulation in the major blood vessels of the heart.
Balloon angioplasty is the most common endovascular procedure (procedure performed inside the blood vessel) carried out to treat coronary artery disease. In this procedure, the blood clots in the major arteries of the heart are detected and cleared by inserting a catheter into an artery of the hand (radial artery) or leg (femoral artery). This catheter consists of a balloon at its tip, which dislodges the clot to the periphery of the blood vessel after inflation.
Angioplasty may or may not be followed by coronary stent placement, depending on the angiography findings. This procedure is performed in patients with fewer blood clots in the vessels and those who do not respond to medications. It may also be carried out as an emergency procedure to treat a heart attack.
Step 1: Placing the patient on oral sedatives
Step 2: Administration of general anaesthesia
Step 3: Incision at the femoral artery or radial artery
Step 4: Insertion of catheter into the artery through an incision
Step 5: Guiding the catheter up to the base of the coronary artery
Step 6: Insertion of a guidewire from within the catheter into the artery up to the site of the blood clot
Step 7: Insertion of contrast dye through the catheter
Step 8: Checking for the blocks through a radiograph
Step 9: Identifying the pinpoint location of the blood clot
Step 10: Passage of guide wire through catheter just beyond the region of clot
Step 11: Inflating and deflating the balloon till normal blood flow is obtained from the vessel
Step 12: Stabilizing the stent in place
Step 13: Retrieving the catheter
Contraindications: You may not be suggested to undergo balloon angioplasty if the access vessel (femoral or radial artery) is of insufficient size and quality.
Recovery time: You will be discharged from the hospital in one day. But you should avoid strenuous activities for one month after being discharged from the hospital.
Prognosis: According to research, 79 percent of the people who receive the stent after a balloon angioplasty are relieved from angina for up to 5 years.
Ask your healthcare adviser for the best multiple options and choose the one that meets your expectations
The average cost of Angioplasty in South Korea starts from USD 18500 Only some of the best and certified hospitals in South Korea perform Angioplasty for international patients.
The cost of Angioplasty in South Korea may differ from one medical facility to the other. The top hospitals for Angioplasty in South Korea covers all the expenses related to the pre-surgery investigations of the candidate. The Angioplasty cost in South Korea includes the cost of anesthesia, medicines, hospitalization and the surgeon's fee. Post-surgical complications, new findings and delayed recovery may have an impact on the total Angioplasty cost in South Korea.
There are several best hospitals for Angioplasty in South Korea. The top hospitals for Angioplasty in South Korea include the following:
The recovery of the patient many vary, depending on several factors. However, on an average, patient is supposed to stay for about 18 days in the country after discharge. This time frame is important to ensure that the surgery was successful and the patient is fit to fly back.
There are certain expenses additional to the Angioplasty cost that the patient may have to pay for. These are the chanrges for daily meals and hotel stay outside the hospital. The extra charges may start from USD 50 per person.
Some of the cpopular cities in South Korea that offer Angioplasty include the following:
After the Angioplasty takes place, the average duration of stay at the hospital is about 2 days. The patient is subjected to several biochemistry and radiological scans to see that everything is okay and the recovery is on track. After making sure that patient is clinically stable, discharge is planned.
There are more than 1 hospitals that offer Angioplasty in South Korea. These clinics have propoer infrastructure as well as offer good quality of services when it comes to Angioplasty Also, these hospitals follow the necessary guidelines as required by the medical associations for the treatment of Angioplasty patients.
Some of the top doctors for Angioplasty in South Korea are: