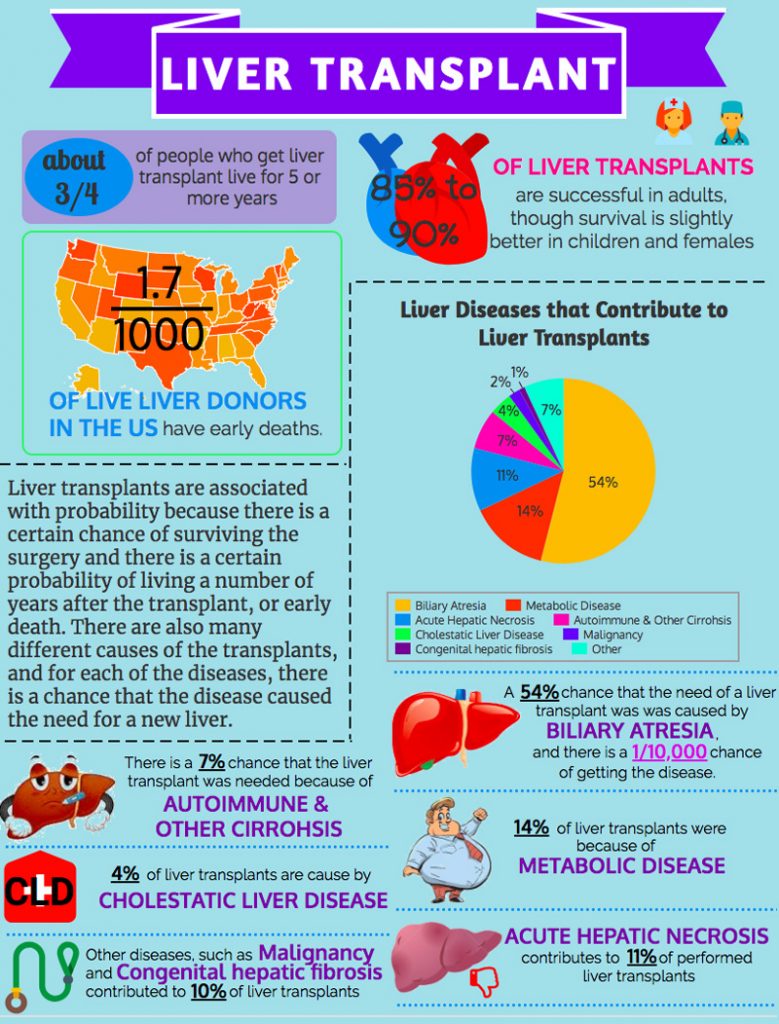
The demand for different organs is increasing around the world. The act of organ transplantation is a boon to the healthcare industry. It has helped save the lives of millions of people around the world suffering from organ failure or last-stage organ disease.
There are several apprehensions in the mind of the people who think of donating an organ. They are particularly worried about how ethical it is, whether their health would get affected, or if they are actually eligible for it. One of the biggest cause of concern for them is the legal formalities. People are unclear about the organ donation laws in their own country, let alone the other countries.
The need for different organs, including lungs, heart, kidneys, and liver far increases the supply of the organs. Therefore, there is a need to promote organ donation by providing the correct information to people and motivating them to join the noble cause of saving the lives of other people in need of an organ.
This has led to the formulation of organ donation laws in all countries to account for this disparity. Apart from making things clear for the donors and people willing to become a donor, such organ donation laws also make sure that the available organ goes to the most deserving recipient and the one who would likely to benefit from it the most.
This article talks about liver transplantation trends across the world and liver donors. Additionally, it explores some of the basic formalities that donors and recipients are required to complete before the surgery takes place.

Check Out Popular Destinations and Top Hospitals for Liver Transplant
Explore Hospitals
Liver Transplant: Why It Has Been A Challenge So Far
Complications arising out of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is the number one indication for liver transplantation. The researchers predict that in the near future, non-alcoholic steatohepatitis cirrhosis complicated by hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is going to be the number one indication for liver transplantation.
Considering the increasing prevalence of end-stage liver disease and liver failure patients, one of the biggest challenges is the huge gap between demand and supply. This is the reason why many liver disease patients requiring an organ are sometimes treated with methods other than transplantation. However, such treatment modalities do not have great success rates.
Some of the other challenges associated with liver donation and transplantation include the following:
- Maintaining a patient on life support system purely for the purpose of extraction of the liver is tedious and complex.
- The use of cadaveric donors is not allowed and culturally accepted in some parts of the world.
- The waiting list for liver transplantation is much extensive. The mortality rate among the patients on the waiting list is, thus, high.
Why Liver Transplant Is Different From Other Organ Transplants?
Liver transplantation is different from other types of transplants. In the case of other transplants, including lung, kidney, and heart transplant, the entire organ is removed from the donor and transplanted into the body of the patient. However, this is not the case in liver transplant surgery.
During a liver transplant, only a piece of liver is retrieved from the donor and transplanted into the body of the patient. This is because the liver has the capability to regenerate and grow rapidly to restore the normal functioning of the organ.
Therefore, in the case of cadaveric liver transplant, the complete liver can be removed because the donor is no longer alive. In the case of living liver donor transplant cases, only a part of the liver is removed, which grows back to its original capacity soon.
Usually, it is safe to remove nearly 70 percent of the liver from the body of the living donor. The remaining portion of the liver grows back to its fully functional capacity within a few days.

Know More about Recovery and other details about the Liver Transplant Treatment
Know More
Human organ transplantation was illegal until a few decades ago. Slowly, different countries across the world started to realize the need to legalize human donation. Efforts intensified to save the lives of the people suffering due to end-stage organ disease or organ failure.
Before the implementation of the Human Organ Transplantation Act across different countries, unrelated organ transplantation was being conducted. This has complications of its own. The implementation of the act was done to curb the two long-standing complications in the field of organ transplantation. One is unrelated to organ donation and the other is the legalization of brain stem death.
Now a majority of the countries in the world go by the revised definition of death – the cessation of the activity of the brain stem. Thus, the organs of the people who have been declared brain dead can now be used for transplantation purpose. However, this can happen only if the patient was a registered organ donor. It can also happen if the family of the donor has given the consent to the hospital to retrieve organs for donation.
The legal formalities for liver donation in India and other countries depend on the approach for donation. Liver transplantation can do done using a cadaveric donor or a living donor.
Irrespective of whether the organ comes from a living or a brain-dead donor, the patients with transplanted liver lead a healthy and normal life. However, the individual outcomes for every patient cannot be generalized as it depends on different factors.
The following are some of the basic legal formalities that must be fulfilled for successful organ donation:
- The donor should have a matching blood type. Having a relative or someone from the immediate family for liver donation is not mandatory. However, the blood type of the donor and the recipient should match. The decision as to whether a person (living or brain dead) is a good donor match lies with the doctor and the information fed into the organ donor registry.
- Overweight and pregnant donors are not considered for liver donation. However, a candidate who has lost weight before donation can still be considered.
- Legally, only donors who are between 18 to 65 years of age are allowed to opt for liver donation. Additionally, they should have overall good health with no current or history of major illness. Also, it is mandatory for them to stay away from smoking for at least 6 weeks before the surgery.
- It is mandatory for the donor to be in sound health to give consent for organ donation. They should be able to understand all the instructions and be capable of undergoing preparation required before the surgery.

Could not Find What You are Looking For
We Can Help
Cadaveric and Living Liver Organ Donation
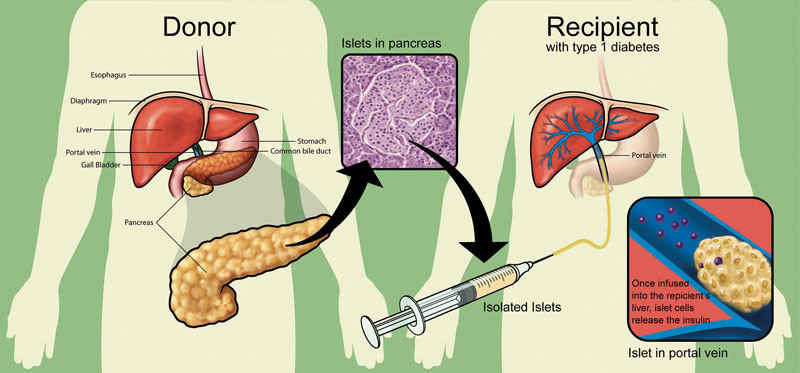
- In case of cadaveric liver donation, there must be a proof in the organ donation registry database or physical documentation proving that the brain-dead person is a registered donor. For non-registered brain-dead patients, the immediate family members must give their written consent for organ donation.
- In case of living donor liver transplant, a thorough medical evaluation is performed after the evaluation of the recipient. A surgery date is scheduled only when the transplant team approves the patient for donation.
- The evaluation includes a confirmation of the blood type and a series of other tests. This includes a chest X-ray, abdominal ultrasound, and an electrocardiogram (EKG or ECG). The prospective living donors are also given a detailed form to fill. This form has questions about their lifestyle, medical history of the family, and current medical status.
- It is also legally necessary to undergo the evaluation from a doctor assigned by the hospital who is not a member of the transplant team. For legal reasons, the same doctor continues to act as a “donor advocate” throughout the procedure and beyond.
Lastly, each country has their own law when it comes to organ donation. It is, therefore, always better to research and gain knowledge about the country-specific rules and regulations.




