What is Blood Cancer
Blood cancer is a malignant condition in which the blood cells lose their ability to function normally and grow out of control, hindering the function of normal blood cells.
Blood cancer typically starts in the cells that procedure different types of blood cells, also known as the bone marrow. The different types of blood cells include red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. The cancer may also form in the cells produced by the marrow, such as lymphocytes or plasma cells (type of white blood cells). The normal blood production by the bone marrow is put to a halt as a result of the growth of abnormal types of (malignant) cells in the blood-forming tissue.
Blood cancer can be differentiated into three main categories or types:
1. Leukemias
Leukemia is a type of blood cancer that starts in the bone marrow and blood. It is the most common type of blood cancer that is characterized by excessive production of white blood cells that do not function properly or inadequate production of platelets and/or red blood cells.
There are different types of leukemia, differentiated based on how aggressive it is and what type of cells are involved. Some of the most common types include the following:
Acute/chronic leukemia: Acute leukemia is characterized by blasts, which are immature blood cells. It needs to be treated immediately because of its aggressive nature. The blast cells can proliferate quickly and indicate defective function. On the other hand, more developed cells that can temporarily function normally are involved in chronic leukemia. In this case, the condition can go undiagnosed for a few years. They develop and divide slowly and symptoms may not appear for a while.
Lymphocytic leukemia: This type of leukemia affects the lymphocytes, which form a part of the lymphatic tissue, which is in turn responsible for immunity.
Myelogenous leukemia: This type of leukemia affects the myeloid cells, which are responsible for the production of red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets.
Some of the most common forms of leukemias based on the categories defined above include the following:
- Acute lymphocytic leukemia (ALL)
- Acute myelogenous leukemia (AML)
- Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL)
- Chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML)
- Others: Myeloproliferative disorders, myelodysplastic syndromes etc.
2. Lymphomas
One kind of blood cancer that affects the lymphatic system is called lymphoma. The lymphatic system is responsible for both the body’s removal of extra fluid and the synthesis of immune cells. The white blood cells called lymphocytes, which are in charge of defending against infections caused by pathogens, are the main objective of this particular type of cancer. The malignant lymphocytes eventually develop into lymphoma, which grows aggressively in the lymph nodes and other tissues in the body.
Further, there are two main types of lymphomas:
Non-Hodgkin’s Lymphoma: It is a type of lymphoma that develops in lymphocytes.
Hodgkin’s Lymphoma: This type of cancer also develops in the lymphocytes but is characterized by a particular type of abnormal lymphocyte called the Reed-Sternberg cell.
3. Multiple Myeloma
Myelomas, also known as multiple myeloma, is a cancer that affects the plasma cells, which are responsible for forming disease-fighting antibodies in humans. These are a type of white blood cell. Myeloma is also known as multiple myeloma since the malignant plasma cells are often present at multiple locations.
Because multiple myeloma affects the formation of plasma cells, the person’s immune system is severely compromised, making them more vulnerable to infections.
Depending on the kind of heavy and/or light chain antibodies that the afflicted plasma cells produce, myeloma can be further classified into different types.
Symptoms and Causes of Blood Cancer
Irrespective of the type of blood cancer, some of the common symptoms include the following:
- Swelling in the lymph nodes
- Frequent, severe, or recurrent infections
- Weakness and unexplained weight loss
- Shortness of breath
- Skin redness, itching, or rashes
- Persistent and chronic fatigue
- Bone pain or joint pain
- Unexplained fever
- Night Sweat
- Excessive bruising or bleeding that does not stop
- Chest pain or abdominal pain
- Coughing
- Loss of appetite and nausea
All types of blood cancers, even those that are inherited, are a result of genetic mutation in the normal DNA in the blood cells. These mutations may result because of a variety of reasons, including the following:
- Exposure to certain industrial chemicals and radiation
- Advancing age
- Excessive smoking
- Family history of blood cancers or any other form of cancer
- Previously received cancer treatment
- History of autoimmune disorders
- Weakened immune system
- Presence of genetic disorders
Tests Conducted Before Blood Cancer Treatment
Several diagnostic tests are required to be done before a firm diagnosis can be established and the treatment protocol for the patient can be decided.
Some of the tests that are required to be completed before the diagnosis of the patient can be concluded include the following:
- Physical examination and observation
- Biochemistry tests (blood tests)
- Bone marrow biopsy
- Lymph node removal and biopsy
- Radiological imaging tests, including X-ray, PET scan, and CT/MRI scan
There may be some additional tests that may be required based on the clinical status and past medical history. These tests may or may not be directly linked to blood cancer.
A biopsy is necessary for cancer staging, which is a crucial factor in determining the kind and stage of the disease. This is often accomplished by taking measurements of the tumor’s size and location and comparing results with those of previous studies.
Since blood cancer is different from solid tumors, it uses a different staging system. This particular technique involves the volume of blood present, swelling of the liver or spleen, size and quantity of abnormal malignant cells, genetic abnormalities, and degree of bone damage. The outcome of this assessment is then correlated with the information retrieved from the radiological scans.
Apart from staging, grading of the blood cancer is performed in the case of lymphomas. Grading helps identify whether the cancer is high-grade, intermediate-grade, or low-grade.
Procedure-Wise Cost of Blood Cancer Treatment in India
Factors Affecting the Blood Cancer Treatment Cost in India
The cost of treating blood cancer is influenced by several factors, including the type of treatment, how long it takes, and many other intricate details.
Some of the most common factors affecting the cost of blood cancer treatment include the following:
- Type of blood cancer
- Rate of spread
- The stage at which the patient has been diagnosed
- Clinical status of the patient
- Family history
- Treatment history
- Severity of symptoms
- Type of diagnostics advised
- Type of treatment/regimen advised
Some of the other factors such as patient location and demographics and geographical availability of the treatment also matter in terms of the overall cost of treatment that a patient is likely to pay.
Treatment Options for Blood Cancer Treatment in India
There are many parameters that are taken into consideration before planning for the treatment of patients.
Some of the factors that are taken into consideration before subjecting the patient to any type of treatment for blood cancer include the following:
- Current blood cell counts
- Symptoms
- Overall health and clinical status
- Type of blood cancer
- Stage of cancer
- Genetic test results
Blood cancer treatment in India is available at several multi-super specialty hospitals. Many patients from countries around the world travel to India for treatment of blood cancer in India because almost all new techniques and approaches used for treatment are available.
The following are some of the most common forms of blood cancer treatment available in India:
1. Chemotherapy

Chemotherapy involves the use of drugs with the potential to kill cancer cells. It is usually administered directly into a vein through an intravenous drip and from there, the drug circulates in the blood.
This treatment is usually administered on an outpatient or daycare basis. That is, the patient is admitted in the morning to receive a bagful of fluid containing a single drug or a combination of drugs intravenously and then discharged in the evening. Sometimes, especially in the case of children, hospital admission may be necessary to receive the drugs to enable better monitoring and care.
The chemotherapy drug dosage is usually split into a few cycles, which are given at an interval of 7/14/21 days. The combination of drugs received by the patient is primarily decided based on the type of blood cancer that the patient is suffering from, the overall physical status, etc.
2. Immunotherapy
This is a relatively newer type of treatment in which the doctors give certain drugs to harness the capability of the immune system of the patients to fight the abnormal blood cancer cells. It also boosts the functioning of the immune system in the patients.
Monoclonal antibody treatment is one common form of immunotherapy that is available and applied in India. Rituximab is one common immunotherapy drug used in patients.
The immunotherapy drugs work by attaching themselves to the cancer cells, which makes it easier for the body’s natural immune system to identify it as a foreign cell, and therefore, it kills it.
Another type of immunotherapy technique available is CAR-T cell therapy, which is a newer form of treatment. In this type of treatment, the patient’s T-cells are genetically modified to boost their capacity to identify and kill cancer cells. This therapy, at the moment, is not available in India.
3. Targeted Therapy
Targeted therapy works by identifying the genetic mutations or changes in the cancer cells and thereby targets the cells based on it. These are drugs that are usually given intravenously, either along with chemotherapy or as a standalone treatment.
4. Bone Marrow Transplantation

Bone marrow transplantation is a complex and intensive procedure that involves long hospitalization. In this treatment, the diseased stem cells contained inside the bone marrow are replaced with healthy, blood-forming stem cells.
All blood cells once stem cells in their early stages of development. Blood cancer eventually results when something goes wrong during their development and eventually, it develops into blood cancer.
A bone marrow transplant, also known as a stem cell transplant, is a treatment that can be applied to certain types of blood cancer patients. Often, such patients receive chemotherapy first to destroy the diseased blood cancer cells and the abnormal stem cells. Then, once the patient is in remission or a disease-free state, he or she receives a fresh set of healthy stem cells that migrate and start functioning by producing healthy blood cells.
A bone marrow transplant can also be required once a patient receives high-dose chemotherapy. This is because chemotherapy destroys diseased as well as healthy bone marrow, which ultimately has to be replaced.
5. Radiotherapy
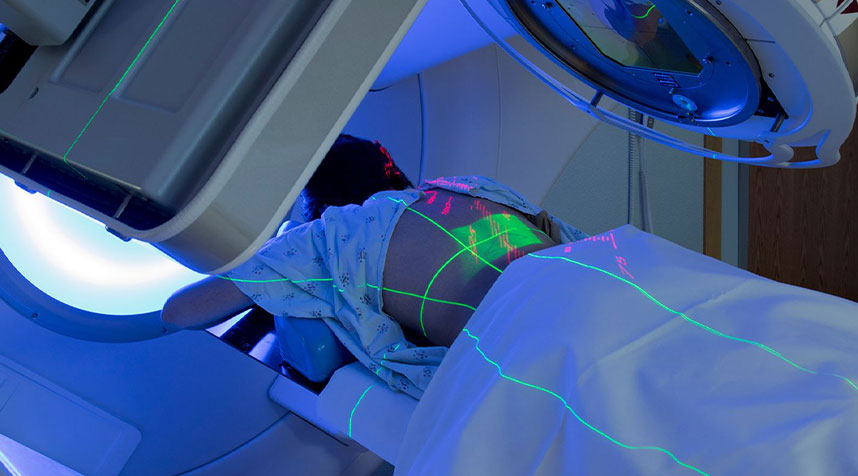
Radiotherapy is sometimes used as a part of the overall treatment protocol for patients suffering from Lymphoma. In this treatment, high-energy rays are targeted at the area where blood cancer cells are accumulated, primarily certain lymph nodes. Doing so helps kill the cancer cells which also controls the pain associated with cancer.
>>How a Donor Matched with the Patient for a Bone Marrow Transplant?
The allogeneic transplant involves transplanting bone marrow from a donor. Before this process can begin, certain tests have to be performed to confirm that the donor is a suitable match. This is important to minimize the chances of side effects like GVHD or graft vs host disease.
When a patient’s immune system attacks transplanted tissue from a donor as it perceives it as foreign, GVHD results. This may put the patient’s life in danger. The medical staff assesses the donor’s level of physical fitness. To avoid a mismatch, HLA typing is done
This is the most important test used to determine if the donor is a match for the patient. HLA or human leukocyte antigens are proteins present on the surface of most of the cells inside your body. The immune system uses these as markers to identify if the cells belong in your body or not. HLA match between the patient and donor minimizes the risks of side effects. HLA testing can be done from a blood sample or a cheek swab.
Blood Cancer Survival rate in India
Leukemia life expectancy varies according to the patient’s age, the kind of leukemia, and other variables. Although there is currently no cure for leukemia, the malignancy can be treated to help improve prognosis.
Recent research indicates that the 5-year survival rate for children with acute lymphocytic leukemia (ALL) is currently approximately 90%. However, the likelihood of surviving five years or longer with leukemia may be lower for other types.
The reasons that dictate the blood cancer survival include the following:
- Age of the patient
- Stage and grade of cancer
- Type of blood cancer
- Family history
- Past medical history
- Clinical status of the patient
- At which stage cancer has been diagnosed
Hospitals for Blood Cancer Treatment in India
Best Doctors for Blood Cancer Treatment in India
BMT Package for Blood cancer Treatment in India
Why Choose India for Blood Cancer Treatment
There are several reasons that make India a lucrative destination for blood cancer treatment. Some of the top reasons include the following:
- State-of-the-art hospitals with infrastructure, diagnostic and treatment facilities as required by the patients
- Highly qualified hematologists and hemato-oncologists, many of them are trained from some of the best institutes in the world and are a part of prestigious professional organizations
- The cost of blood cancer treatment in India is much less compared to other countries offering the same treatment options, technology and standard of care
- India is well-connected to the rest of the world through direct and indirect flights
- Since blood cancer treatment generally involves a long duration of stay, the low cost of living in India does not have a significant impact on the budget of the patient
FAQ’s
The average survival rate in case of leukemia is between 60 and 80 percent. The overall survival could be more or less, depending on factors such as age of the patient, type of leukemia and the stage of cancer.
It is possible to control the spread of CML. In some cases, it is possible to completely cure it as well. However, it is best to discuss the prognosis and outcomes with the treating doctor at the time of discussion related to the treatment plan.
Cancer is not contagious and therefore, it cannot be transferred from one patient to another. However, it can be inherited in certain cases.
Yes, It is possible to treat blood cancer completely in certain cases. However, the rate of success can only be determined on the basis of proper assessment of the patient, clinical status, treatment history, age, blood cancer type and several other parameters.
The hospital stay depends on the type of treatment that the patient is receiving. It may range from a couple of days to about one month, depending on the treatment type. To complete the entire course of treatment, the patients are required to stay, on average, for about two to three months.
Apart from the treatment cost, the patient and the family members are expected to bear the cost of accommodation for their stay in the country, the feeding cost, the cost of discharge medicines, and any additional expenses associated with the treatment of a new diagnosis or complications arising out of the health situation.